Last Updated on July 10, 2020 by Arpit Singh
The fire triangle is the simplest scientific explanation of what it takes to start and sustain a fire. In order to understand how does, it works it is better we study first what fire is and what does it mean.
In ancient times Greeks considered fire, earth, water, and air as a major element in-universe. One can feel fire just as one can feel the earth, water, and air. You can smell it and transfer it from one place to another.
But the fire is really something peculiar. In which category would you place fire in, Solid, Liquid, Gas or Plasma? (Take a moment to think!)…
It’s not unusual to guess fire as the gas based on our primary knowledge of different states of matter. But on a more scientific level, it is not. Unlike the fire, a gas will exist in its raw state but the fire eventually burns out.
One common misconception is that fire is in fact the forth state of matter i.e plasma. It is said based on the science that in plasma atoms are stripped of their electron, just like in a fire. But unlike other forms of matter plasma is unstable and does not exist on earth.
Plasma forms under controlled laboratory conditions when gas molecules are exposed to superheated temperatures or high power electric field.
These required temperatures range anywhere from a thousand degrees to tens of thousands of degrees Celcius. In contrast, a wood fire or fire from a burning paper burn at just a few hundred degrees.
Then How Do You Explain Fire?
So, if fire isn’t a solid, liquid, gas or plasma, what is it then? It turn out fire isn’t actually a matter at all instead it’s our sensory experience of chemical reaction called combustion.
You may understand it better with an example, it’s like the smell of apple which is ripening. Combustion/burning is a chemical reaction, which stimulus our sense that a chemical reaction is taking place.
What is different about fire is that it involves several of our senses at the same time and creates a clear sense of experience ( heat, shape, smell, sound ) that we generally expect from physical things. The burning of fire creates this sensory stimulation using fuel. Heat and oxygen.
Understanding With A Practical Example
Let take an example of a wood fire to make it more clear. When you heat the wooden log to their ignition temperature the walls of their cells start to decompose breaking into simpler compounds and molecules.
These molecules then react with air oxygen to create carbon dioxide and water, at the same time any trapped water in the logs vaporizes, expands, ruptures the wood around it, hence creating that soothing cracking sound.
As we heat up the wood, the rise in temperature causes the decomposition of the wood which result in giving off of vapor molecule, these molecules of vapor breaks down into individual atom and combine again with oxygen to form a new molecule.
It is during this process that energy is given off when breaking and recombining of these atom occurs.
The heat which is released during burning is called Radiant Heat, which is pure energy. It’s the same heat we feel from sun radiates. Part of this radiant heat moves back to the seat of the fire, this radiant heat which radiates back to the fuel is called Radiation Feedback.
Fire Triangle And The Chemistry of fire
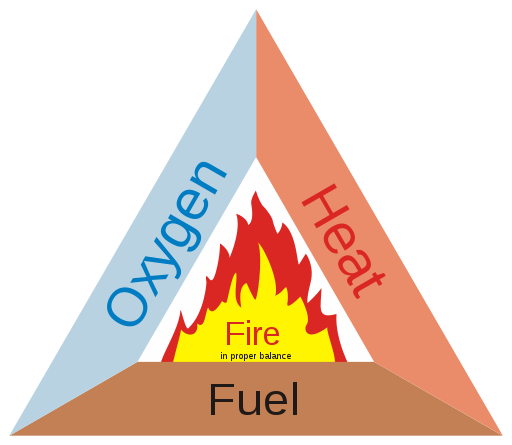
Fire triangle: It includes three (sides of a triangle) elements, Air (oxygen), Fuel (Combustible material), and Ignition(Source of heat).
Fire Triangle shows that three elements are required for a fire to burn and if anyone of the side of the triangle is removed the fire will cease to exist.
The air that surrounds us all contain 21% oxygen by volume and it takes just 16% of oxygen to start a fire. Similarly we will find source of fire radially available like the wood, oil fuel, dry grass, wood piles, paper etc.
So it is the heat source which at many times responsible to start a fire. In addition to the fuel source and air, it’s the major part of this fire triangle that helps start and sustain any fire.
All flame source when burn produces heat and thus are self-sustaining once they start to burn till either the supply of air is cut or the source of their fuel is consumed. This can be better stated as the combustion chain reaction.
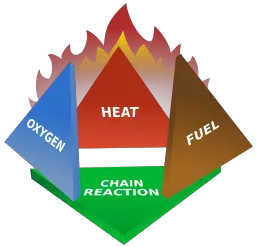
Air, fuel and heat represent the fire triangle; now add chain reaction to it you get fire tetrahedron. Fire Tetrahedron shows that the chemical reaction (Chain reaction) is essential for the fire to keep on burning.
What is Chain reaction ?
The chain reaction is like a positive feedback loop for fire. We know that most of the material gives off vapor which catches fire except coal.
The fire which is already burning is and chemical reaction which emits or give of heat (i.e Exothermic Chemical reaction).
The heat is given off by the fire heat-up the material which is already burning to give off even more volatile vapor. If this positive feedback loop is ‘Inhibited’ by any means, it would result in extinguishing of the fire.
Difference Between the Fire Triangle and Fire Tetrahedron
The fire triangle is a simple means of illustrating the three requirements for the existence of fire. However, it does not explain the nature of the fire.
In particular, it does not include the chain reaction that results from chemical reactions among the fuel, oxygen, and heat. It is the factor which does not start the fire but sustain it.
The fire tetrahedron is a better representation of the combustion process. ( The diagram is better in the sense that it allows us to learn the role of the combustion process in an illustrative form).
The basic difference between the fire triangle and the fire tetrahedron is this: The tetrahedron illustrates how flaming combustion is supported and sustained through the chain reaction.
In a sense, the chain reaction face keeps the other three faces from falling apart.
This is an important point because the extinguishing agents used in many modern portables fire extinguishers, automatic extinguishing systems, and explosion suppression systems directly attack and break down the chain reaction sequence.
Different Classes OF Fire
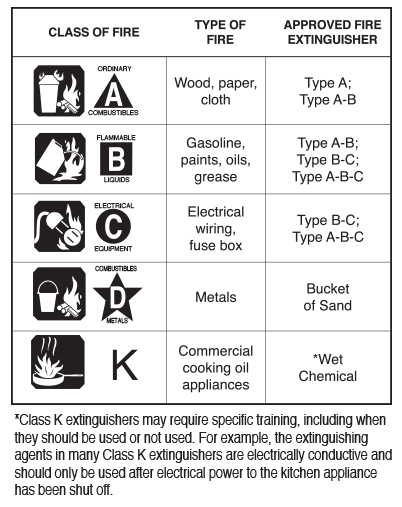
According to the European Standard for Classification of Fire 1992/2004; fires can be classified into five major types based on the type of fuel source. These types of fire can be classified into Class A, B, C, D, and F types.
Class A fire represents the everyday ordinary fire from wood, paper, textiles, PVC, dry crops and cartons. Class B is for fire produced from combustible liquids such as the gasoline.
Class C fire is for combustion of gases and D is for combustion of highly reactive metals. While Class K represents fire from cooking medium; fat and vegetable oil.
It is these classes of fire that determines the sub-types of different fire extinguishers. Type of fire extinguisher used on board vessel are classified as below:
- Portable fire extinguisher
- Semi-portable fire extinguisher
- Fixed type of fire fighting equipment
How fire occurs on-board ship?
Fire will burn as long as there is something to burn, Oxidation is a chemical process in which a substance combines with oxygen. As it’s an oxidation reaction, energy is given off in the form of heat.
If you remembered chemistry that has been taught in high school, rotting of wood or rusting of iron is some common example of slow oxidation.
Combustion/burning/fire is an example of rapid oxidation, the vapor of substance combines with oxygen at a very high rate, we can see and feel the energy in form of light(as a flame) and heat(rise in temperature)
There are myriad of ways that fire may occur on-board, few of them are mentioned here.
- In accommodation: At the top of any list of fire causes aboard ship is careless smoking. Glowing ashes or the tobacco contain enough heat to start a fire in paper, cardboard, excelsior, rope, and bedding. Then there is the risk of electric fire from sort circuit and overloading.
- In Cargo-Space: Smoking or source of fire in cargo space is an invitation to disasters. Cargo holds should be monitored closely during unloading and loading operations. In the case of Ro-Ro vessel which has thousands of cars for transfer, close monitoring becomes even more vital, because each car has a battery ready to start a major fire.
- In Engine room: Engine room may be considered as the favorite place of Miss. Fire, as the engine room has all the requirements to fulfill the fire triangle. If care is not taken the oily rags that are disposed of in the dumping bin may catch fire. Whichever component which is moving/rotating/transferring high temperature or flammable substance is a possible cause of the fire.
How to extinguish fire?
From the fire triangle/tetrahedron we know it takes three/four elements to support fire, hence removing any one side of the triangle will help in extinguishing the fire.
Removing Heat from fire is called Cooling (Removing heat means cooling)
Removing Fuel from fire is called starving. (Fuel is like food for fire, if fire don’t eat fuel it will starve to death).
Removing Oxygen from fire is called Smothering (Oxygen is air for fire, if a fire doesn’t get the oxygen it will smother). This is the same science acting behind using a blanket to cover the fire.
Removing Chemical reaction from fire is called Inhibiting. This method if employed will extinguish the fire immediately when properly employed.
Reference Sources: TEDX Video On Fire, Scribd Resources On Fire, Marine Book on – Fire Prevention, fire fighting and fire safety.
Also Read:
- Flammability Diagram And Its Application in Tankers
- CO2 Flooding System – Fixed Fire Fighting System Ship
- Flame Arrester – It’s Working & Why Is It Required
- Fire Detector Types And Their Working Principle